Exploring Hardware: A Comprehensive Overview
Tectoks: Your Ultimate Guide to Hardware Exploration Dive into a comprehensive overview of the latest trends and advancements in the world of hardware.

Table of Contents:
-
Introduction
-
Computer Hardware Basics
-
Computer Hardware Components
-
Types of Computer Hardware
-
Computer Hardware Future
-
Conclusion
1. Introduction
Computer hardware is the term that refers to the physical components of a computer system, such as the circuit boards, chips, wires, cables, and devices that make up the machine. Computer hardware is different from computer software, which is the set of instructions and programs that run on the hardware and perform various tasks.
The history of computer hardware can be traced back to the early attempts to create mechanical calculators that could perform arithmetic operations. The first known device of this kind was the abacus, which was invented by the ancient Babylonians around 2500 BC. The abacus used beads and rods to represent numbers and perform calculations. Later, in the 17th century, several inventors designed and built more advanced mechanical calculators, such as the Pascaline by Blaise Pascal, the Stepped Reckoner by Gottfried Leibniz, and the Difference Engine by Charles Babbage. These machines used gears, wheels, levers, and springs to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
The development of computer hardware took a major leap in the 19th and 20th centuries with the invention of electricity, electronics, and digital logic. These technologies enabled the creation of electronic computers that could store and process data using binary digits (bits) and logic gates. Some of the pioneers of electronic computing were John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry, who built the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC) in 1939; Konrad Zuse, who built the Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4 computers between 1936 and 1945; and John von Neumann, who proposed the stored-program architecture for computers in 1945. The first generation of electronic computers used vacuum tubes and relays as the main components, such as the ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, and EDSAC. The second generation of electronic computers used transistors and diodes, which were smaller, faster, and more reliable than vacuum tubes, such as the IBM 1401, DEC PDP-1, and CDC 1604. The third generation of electronic computers used integrated circuits (ICs), which were tiny chips that contained thousands of transistors and other components, such as the IBM System/360, DEC PDP-8, and Intel 4004. The fourth generation of electronic computers used microprocessors, which were single-chip ICs that contained the entire central processing unit (CPU) of a computer, such as the Intel 8080, Motorola 6800, and Zilog Z80. The fifth generation of electronic computers used very large-scale integration (VLSI) and ultra large-scale integration (ULSI) technologies, which allowed millions and billions of transistors to be packed on a single chip, such as the Intel Pentium, AMD Athlon, and ARM Cortex.
The purpose and importance of computer hardware are to enable the execution of computer software and the performance of various tasks and functions. Computer hardware is essential for many applications and domains, such as education, entertainment, communication, business, science, engineering, medicine, and more. Computer hardware can help people learn new skills, access information, play games, watch movies, listen to music, send and receive messages, store and manage data, perform calculations, design and create products, control and monitor systems, diagnose and treat diseases, and more.
The main topics of this blog are computer hardware basics, computer hardware components, types of computer hardware, and the future of computer hardware. In the following sections, we will explore these topics in more detail and learn more about the fascinating world of computer hardware.
2. Computer Hardware Basics
Here is a possible explanation for the computer hardware basics section of the blog:
One of the fundamental concepts of computer hardware is the input-output (I/O) model, which describes how computer hardware interacts with the external environment and performs various tasks. The I/O model consists of four basic functions and operations: input, output, processing, and storage.
-
Input: Input is the function of receiving data or information from external sources, such as the user, the network, or the sensors. Input devices are the hardware components that enable input, such as the keyboard, mouse, microphone, camera, scanner, etc. Input devices convert the data or information into binary signals that can be understood by the computer hardware.
-
Output: Output is the function of sending data or information to external destinations, such as the user, the network, or the actuators. Output devices are the hardware components that enable output, such as the monitor, speaker, printer, projector, etc. Output devices convert the binary signals from the computer hardware into data or information that can be perceived by external recipients.
-
Processing: Processing is the function of manipulating, transforming, and analyzing the data or information that is input or output by the computer hardware. Processing devices are the hardware components that enable processing, such as the CPU, GPU, FPGA, ASIC, etc. Processing devices execute the instructions and programs that are stored in the computer hardware and perform various operations, such as arithmetic, logic, control, and communication.
-
Storage: Storage is the function of retaining, retrieving, and organizing the data or information that is input, output, or processed by the computer hardware. Storage devices are the hardware components that enable storage, such as the RAM, hard disk, SSD, flash drive, CD, DVD, etc. Storage devices store data or information in different formats, such as bits, bytes, files, folders, databases, etc.
The performance of computer hardware is determined by how well it can perform the four basic functions and operations of the I/O model.
The performance of computer hardware can be measured by various units and metrics, such as speed, capacity, power, and reliability.
-
Speed: Speed is the measure of how fast the computer hardware can perform the input, output, processing, and storage functions and operations. Speed is usually expressed in terms of frequency, latency, bandwidth, and throughput. Frequency is the number of cycles or operations that the computer hardware can perform per second and is measured in hertz (Hz). Latency is the amount of time that the computer hardware takes to respond to a request or complete an operation and is measured in seconds or milliseconds. Bandwidth is the amount of data or information that the computer hardware can transfer or process per unit of time and is measured in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second (Bps). Throughput is the amount of work or tasks that the computer hardware can accomplish or complete per unit of time and is measured in operations per second (ops) or instructions per second (IPS).
-
Capacity: Capacity is the measure of how much data or information the computer hardware can input, output, store, or process at a given time. Capacity is usually expressed in terms of bits, bytes, words, or blocks. A bit is the smallest unit of data or information that the computer hardware can handle and can have only two values: 0 or 1. A byte is a group of eight bits and can represent a character, a number, or a symbol. A word is a group of bits or bytes that the computer hardware can process as a single unit and can vary in size depending on the computer hardware architecture. A block is a group of bits, bytes, or words that the computer hardware can store or transfer as a single unit and can also vary in size depending on the computer hardware design.
-
Power: Power is the measure of how much energy the computer hardware consumes or dissipates when performing the input, output, processing, and storage functions and operations. Power is usually expressed in terms of voltage, current, resistance, and wattage. Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points in the computer hardware circuit and is measured in volts (V). Current is the rate of flow of electric charge in the computer hardware circuit and is measured in amperes (A). Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric charge in the computer hardware circuit and is measured in ohms (Ω). Wattage is the amount of power that the computer hardware uses or produces and is measured in watts (W).
-
Reliability: Reliability is the measure of how well the computer hardware can perform the input, output, processing, and storage functions and operations without errors, failures, or interruptions. Reliability is usually expressed in terms of mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to failure (MTTF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and availability. MTBF is the average time that the computer hardware operates without failure and is measured in hours, days, or years. MTTF is the average time that the computer hardware operates until a failure occurs and is also measured in hours, days, or years. MTTR is the average time that the computer hardware takes to recover or repair from a failure, and is measured in minutes, hours, or days. Availability is the percentage of time that the computer hardware is operational and functional and is calculated by dividing the MTBF by the sum of the MTBF and the MTTR.
The performance of computer hardware is influenced by various factors, such as design, architecture, compatibility, and optimization.
These factors affect how the computer hardware is built, organized, connected, and configured, and how it can be improved or enhanced.
-
Design: Design is the factor that determines the shape, size, structure, and layout of the computer hardware components and devices. Design affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the physical properties, such as weight, dimension, material, and color, and the aesthetic properties, such as style, appearance, and ergonomics. Design also affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the cost, quality, and durability of the computer hardware components and devices.
-
Architecture: Architecture is the factor that determines the logic, function, and operation of the computer hardware components and devices. Architecture affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the data representation, instruction set, addressing mode, and bus system of the computer hardware. Architecture also affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the parallelism, scalability, and modularity of the computer hardware components and devices.
-
Compatibility: Compatibility is the factor that determines the interoperability and integration of computer hardware components and devices. Compatibility affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing communication, coordination, and cooperation of the computer hardware components and devices. Compatibility also affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the standardization, regulation, and certification of computer hardware components and devices.
-
Optimization: Optimization is the factor that determines the improvement and enhancement of computer hardware components and devices. Optimization affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the efficiency, effectiveness, and quality of its functions and operations. Optimization also affects the performance of computer hardware by influencing the innovation, invention, and evolution of computer hardware components and devices.
3. Computer Hardware Components
Computer hardware components are the individual parts or devices that make up the computer system and perform the input, output, processing, and storage functions and operations.
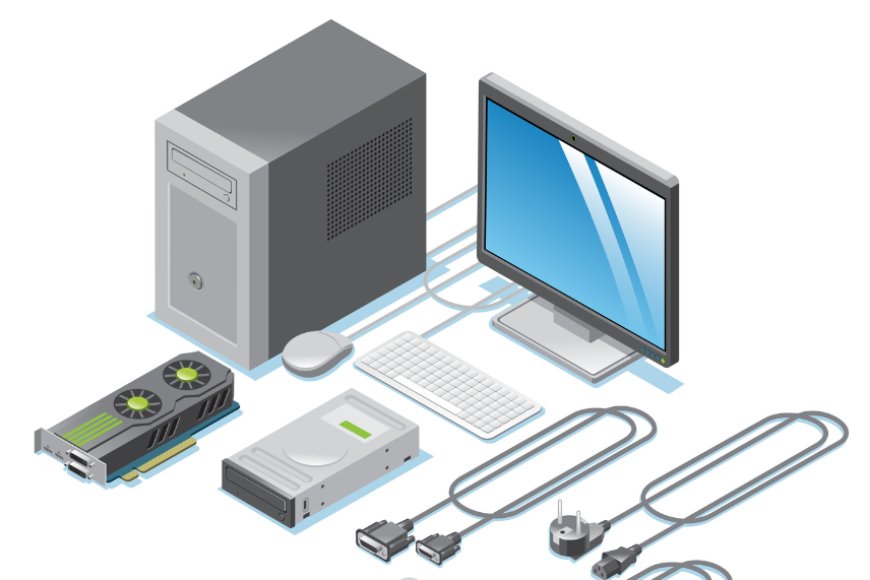

The main components of computer hardware are the motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard disk, GPU, keyboard, mouse, monitor, printer, etc.
-
Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board of the computer system and connects and communicates with all the other components and devices. The motherboard provides power, data, and control signals to the components and devices and also contains the BIOS (basic input/output system), which is the firmware that controls the booting and configuration of the computer system. The motherboard has various slots, sockets, and ports for attaching components and devices, such as the CPU socket, the RAM slots, the PCI (peripheral component interconnect) slots, the SATA (serial advanced technology attachment) ports, the USB (universal serial bus) ports, etc. The motherboard also has various chips and controllers that manage the functions and operations of the components and devices, such as the chipset, the CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) battery, the clock generator, the sound card, the network card, etc. Some examples and illustrations of different models and brands of motherboards are the ASUS ROG Maximus XIII Hero, the MSI MEG Z590 Godlike, and the Gigabyte Z590 Aorus Master. These motherboards are compatible with the latest Intel 11th generation processors and have various features and specifications, such as the LGA 1200 socket, the Z590 chipset, the DDR4 memory support, the PCIe 4.0 support, the Wi-Fi 6E support, the RGB lighting, etc.
-
CPU: The CPU (central processing unit) is the brain of the computer system and performs the processing functions and operations. The CPU executes the instructions and programs that are stored in the computer hardware and performs various operations, such as arithmetic, logic, control, and communication. The CPU consists of two main parts: the ALU (arithmetic logic unit), which performs the arithmetic and logic operations, and the CU (control unit), which controls the flow and timing of the operations. The CPU also has various registers, which are small and fast memory units that store the data and information that are being processed. The CPU also has various caches, which are larger and slower memory units that store the data and information that are frequently accessed by the CPU. The CPU communicates with the other components and devices through the bus system, which consists of the data bus, the address bus, and the control bus. The CPU has various characteristics and parameters that determine its performance, such as the clock speed, the core count, the thread count, the cache size, the instruction set, the architecture, the power consumption, etc. Some examples and illustrations of different models and brands of CPUs are the Intel Core i9-11900K, the AMD Ryzen 9 5950X, and the Apple M1. These CPUs are some of the most powerful and efficient processors on the market and have various features and specifications, such as the 8-core, 16-thread, 5.3 GHz, 125 W, 14 nm, x86-64 Intel Core i9-11900K, the 16-core, 32-thread, 4.9 GHz, 105 W, 7 nm, x86-64 AMD Ryzen 9 5950X, and the 8-core, 8-thread, 3.2 GHz, 10 W, 5 nm, ARM64 Apple M1.
-
RAM: The RAM (random access memory) is the main memory of the computer system and performs the storage functions and operations. The RAM stores the data and information that are input, output, or processed by the CPU and allows the CPU to access them randomly and quickly. RAM is a volatile memory, which means that it loses its contents when the power is turned off. RAM has various types and standards, such as DRAM (dynamic random access memory), SRAM (static random access memory), SDRAM (synchronous dynamic random access memory), DDR (double data rate) SDRAM, DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, the DDR4 SDRAM, etc. The RAM has various characteristics and parameters that determine its performance, such as capacity, speed, latency, bandwidth, voltage, form factor, etc. Some examples and illustrations of different models and brands of RAMs are the Corsair Vengeance RGB Pro, the G.Skill Trident Z Neo, and the Crucial Ballistix. These RAMs are some of the most popular and reliable memory modules in the market and have various features and specifications, such as the 16 GB, 3200 MHz, CL16, 1.35 V, 288-pin, DDR4 Corsair Vengeance RGB Pro, the 32 GB, 3600 MHz, CL16, 1.35 V, 288-pin, DDR4 G.Skill Trident Z Neo, and the 16 GB, 2666 MHz, CL16, 1.2 V, 288-pin, DDR4 Crucial Ballistix.
-
Hard disk: The hard disk is the secondary memory of the computer system and performs storage functions and operations. The hard disk stores the data and information that are input, output, or processed by the CPU and allows the CPU to access them sequentially and slowly. The hard disk is a non-volatile memory, which means that it retains its contents when the power is turned off. The hard disk has various types and technologies, such as the HDD (hard disk drive), the SSD (solid state drive), the SSHD (solid state hybrid drive), the NVMe (non-volatile memory express) SSD, the SATA (serial advanced technology attachment) SSD, the M.2 SSD, the PCIe (peripheral component interconnect express) SSD, etc. The hard disk has various characteristics and parameters that determine its performance, such as capacity, speed, latency, bandwidth, power consumption, form factor, etc. Some examples and illustrations of different models and brands of hard disks are the Seagate Barracuda, the Samsung 870 QVO, and the Western Digital Black SN850. These hard disks are some of the most spacious and fast storage devices in the market and have various features and specifications, such as the 8 TB, 7200 RPM, 256 MB cache, 6 Gbps, 3.5 inch SATA HDD Seagate Barracuda, the 8 TB, 560 MB/s read, 530 MB/s write, 4 KB random read, 98,000 IOPS, and 4 KB random write 88,000 IOPS, 2.5 inch, SATA SSD Samsung 870 QVO, and the 2 TB, 7000 MB/s read, 5100 MB/s write, 4 KB random read 1,000,000 IOPS, 4 KB random write 720,000 IOPS, M.2 2280, PCIe 4.0 x4, NVMe SSD Western Digital Black SN850.
-
GPU: The GPU (graphics processing unit) is the specialized processor of the computer system and performs the processing functions and operations related to graphics, such as rendering, shading, lighting, texturing, etc. The GPU executes the instructions and programs that are related to graphics and performs various operations, such as vector, matrix, and tensor operations. The GPU consists of various parts, such as the cores, the shaders, the memory, the bus, etc. The GPU communicates with the CPU and the other components and devices through the bus system, such as the PCI, the AGP (accelerated graphics port), the PCIe, etc. The GPU has various characteristics and parameters that determine its performance, such as the clock speed, the core count, the shader count, the memory size, the memory speed, the memory bandwidth, the architecture, the power consumption, etc. Some examples and illustrations of different models and brands of GPUs are the Nvidia GeForce RTX 3090, the AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT, and the Intel Iris Xe. These GPUs are some of the most powerful and advanced graphics processors in the market and have various features and specifications, such as the 24 GB, 384-bit, GDDR6X, 19.5 Gbps, 936 GB/s, 10,496 CUDA cores, 1.7 GHz, 350 W, 8 nm, Ampere Nvidia GeForce RTX 3090, the 16 GB, 256-bit, GDDR6, 16 Gbps, 512 GB/s, 5,120 stream processors, 2.25 GHz, 300 W, 7 nm, RDNA 2 AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT, and the 96 execution units, 1.3 GHz, 10 W, 10 nm, Xe-LP Intel Iris Xe.
-
Keyboard: The keyboard is the main input device of the computer system and allows the user to enter data or information, such as characters, numbers, symbols, commands, etc. The keyboard consists of various keys, such as the alphanumeric keys, the function keys, the modifier keys, the navigation keys, the numeric keypad, etc. The keyboard converts the keystrokes into binary signals that can be understood by the computer hardware. The keyboard communicates with the computer hardware through various interfaces, such as the PS/2, the USB, the Bluetooth, etc. The
4. Types of Computer Hardware
Computer hardware is the term used to describe the physical components of a computer system, such as the case, motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard disk, monitor, keyboard, mouse, etc. Computer hardware can be classified into different types based on various criteria, such as size, shape, function, and usage.

Here are some of the common types of computer hardware and their characteristics:
-
Desktop: A desktop computer is a personal computer that is designed to be used on a desk or a table. A desktop computer usually consists of a separate monitor, keyboard, mouse, and computer case that contain the motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard disk, optical drive, and other internal components. A desktop computer is typically more powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a laptop computer, but it is also less portable and requires more space and power. Desktop computers are suitable for tasks that require high performance, such as gaming, video editing, graphic design, etc
-
Laptop: A laptop computer is a personal computer that is designed to be portable and easy to carry around. A laptop computer usually integrates the monitor, keyboard, touchpad, and computer case into one unit that can be folded and closed for transportation. A laptop computer may also have a battery that allows it to operate without a power cord. A laptop computer is typically less powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a desktop computer, but it is also more convenient and versatile. Laptop computers are suitable for tasks that require mobility, such as traveling, working remotely, studying, etc
-
Tablet: A tablet computer is a personal computer that is designed to be handheld and operated by touch. A tablet computer usually has a touchscreen that displays the user interface and accepts input from the user’s fingers or a stylus. A tablet computer may also have a camera, microphone, speaker, and wireless connectivity. A tablet computer is typically less powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a laptop computer, but it is also more compact, lightweight, and user-friendly. Tablet computers are suitable for tasks that require simplicity, such as browsing the web, watching videos, reading e-books, playing games, etc
-
Smartphone: A smartphone is a personal computer that is designed to be both a mobile phone and a computing device. A smartphone usually has a touchscreen that displays the user interface and accepts input from the user’s fingers or a stylus. A smartphone may also have a camera, microphone, speaker, and wireless connectivity. A smartphone is typically less powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a tablet computer, but it is also more pocket-sized, multifunctional, and communicative. Smartphones are suitable for tasks that require connectivity, such as making calls, sending messages, accessing the internet, using apps, etc.
-
Server: A server computer is a computer that is designed to provide services to other computers over a network. A server computer usually has a high-performance CPU, large RAM, a massive hard disk, and a network interface. A server computer may also have a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and other peripherals for administrative purposes. A server computer is typically more powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a personal computer, but it is also more expensive, complex, and demanding. Server computers are suitable for tasks that require reliability, security, and scalability, such as hosting websites, databases, applications, etc.
-
Supercomputer: A supercomputer is a computer that is designed to perform extremely complex and intensive calculations at very high speeds. A supercomputer usually consists of thousands of processors, terabytes of RAM, petabytes of hard disk, and specialized hardware and software. A supercomputer may also have a cooling system, a power supply, and a network connection. A supercomputer is typically more powerful, customizable, and upgradeable than a server computer, but it is also more costly, rare, and specialized. Supercomputers are suitable for tasks that require extreme performance, such as scientific research, weather forecasting, cryptography, etc.
These are some of the common types of computer hardware, but there are also other types, such as embedded systems, wearable devices, gaming consoles, etc. Each type of computer hardware has its advantages and disadvantages, and the suitable scenarios and applications for each type depend on the user’s needs, preferences, and budget. I hope this explanation helps you understand more about the types of computer hardware. ????
5. Computer Hardware Future
Computer hardware is the term used to describe the physical components of a computer system, such as the case, motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard disk, monitor, keyboard, mouse, etc. Computer hardware development is influenced by various trends and challenges, such as miniaturization, integration, innovation, and sustainability. These factors shape the future directions and possibilities of computer hardware advancement, such as quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, optical computing, and biocomputing. These emerging technologies have potential impacts and implications for society, the economy, and the environment.
Here is a brief explanation of each of these aspects:
-
Miniaturization: This is the trend of making computer hardware smaller and more compact while maintaining or increasing its performance and functionality. Miniaturization enables the creation of portable and wearable devices, such as laptops, tablets, smartphones, smartwatches, etc. Miniaturization also reduces the cost, power consumption, and heat generation of computer hardware, making it more efficient and affordable. However, miniaturization also poses some challenges, such as the physical limits of scaling down the size of transistors, the difficulty of cooling and dissipating heat, and the vulnerability of smaller devices to damage and interference.
-
Integration: This is the trend of combining multiple functions and features into a single device or component, such as a system-on-a-chip (SoC) or a system-in-package (SiP). Integration reduces the complexity and redundancy of computer hardware while increasing its performance and functionality. Integration also enables the creation of multifunctional and versatile devices, such as smartphones, smart speakers, smart TVs, etc. Integration also facilitates the communication and interoperability of different devices and systems, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing. However, integration also poses some challenges, such as the compatibility and standardization of different technologies, the security and privacy of data and information, and the reliability and robustness of integrated systems.
-
Innovation: This is the trend of developing new and novel technologies and methods to improve the performance and functionality of computer hardware, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and nanotechnology. Innovation enables the creation of intelligent and adaptive devices and systems, such as voice assistants, facial recognition, self-driving cars, etc. Innovation also enables the exploration and discovery of new phenomena and applications, such as quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, optical computing, and biocomputing. However, innovation also poses some challenges, such as the ethical and social implications of AI and ML, the technical and scientific difficulties of quantum and neuromorphic computing, and the environmental and health risks of nanotechnology and biocomputing.
-
Sustainability: This is the trend of designing and producing computer hardware that is environmentally friendly and socially responsible, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing waste and emissions, and recycling and reusing materials. Sustainability aims to reduce the negative impacts of computer hardware on the environment and society, such as the depletion of natural resources, the pollution of air and water, and the exploitation of labor and human rights. Sustainability also aims to increase the positive impacts of computer hardware on the environment and society, such as the promotion of a green and circular economy, the empowerment of education and development, and the enhancement of quality of life and well-being. However, sustainability also poses some challenges, such as the trade-off between performance and efficiency, the cost and availability of green and recycled materials, and the regulation and enforcement of environmental and social standards.
These are some of the main trends and challenges of computer hardware development, as well as some of the future directions and possibilities of computer hardware advancement. Each of these aspects has potential impacts and implications for society, the economy, and the environment, both positive and negative. Therefore, it is important to understand and evaluate the benefits and risks of computer evolution and to balance the needs and interests of different stakeholders, such as users, developers, manufacturers, regulators, and consumers. I hope this explanation helps you learn more about the future of computer hardware. ????
6. Conclusion
In this blog, we have learned about the types, trends, challenges, and future of computer hardware. We have seen how computer hardware can be classified into different types based on various criteria, such as size, shape, function, and usage. We have also seen how computer hardware development is influenced by various factors, such as miniaturization, integration, innovation, and sustainability. We have also explored some of the emerging technologies and possibilities of computer hardware advancement, such as quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, optical computing, and biocomputing. Finally, we have discussed some of the potential impacts and implications of computer hardware evolution for society, the economy, and the environment.
The main thesis of this blog is that computer hardware is a dynamic and diverse field that is constantly evolving and improving and that it has significant effects and consequences for various aspects of our lives. Therefore, it is important to understand and appreciate the benefits and risks of computer hardware and to be aware and responsible for its use and development.
If you are interested in learning more about computer hardware, here are some recommendations and suggestions for you:
-
Books: You can read some books that explain the basics and principles of computer hardware, such as [Computer Hardware: The Illustrated Guide to Understanding Computer Hardware] by Kevin Wilson, [How Computers Work: The Evolution of Technology] by Ron White and Timothy Edward Downs, and [Code: The Hidden Language of Computer Hardware and Software] by Charles Petzold.
-
Websites: You can visit some websites that provide information and tutorials on computer hardware, such as [HowStuffWorks: Computer Hardware], [Computer Hope: Hardware], and [GeeksforGeeks: Computer Organization and Architecture].
-
Courses: You can enroll in some online courses that teach you the fundamentals and concepts of computer hardware, such as [Introduction to Computer Hardware] by Coursera, [Computer Hardware Engineering] by edX, and [Computer Hardware and Operating Systems] by Udacity.
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog and learned something new and useful. Remember, computer hardware is not just a bunch of wires and chips, but a fascinating and powerful tool that can change the world. Thank you for your attention and interest. Stay tuned for more blogs on computer science and technology.
What's Your Reaction?